Sheet metal fabrication is the process of turning flat sheet metals, typically 0.15 mm to 10 mm thick, into parts and structures of various shapes. The stock materials for this process are flat metal sheets. Sheet metal fabrication is used to create objects such as enclosures, chassis, brackets, stamped features, curls, etc. It is also used for decorative purposes to make patterns in metal sheets.
How Does Sheet Metal Fabrication Work?
The transition from stock material to the finished product usually requires one or more of the following three processes: material removal (cutting), deforming, and assembly. If all these processes are required, they are usually performed chronologically.
Material Removal
This involves cutting out pieces of the stock material to produce the desired shape. For maximum accuracy, speed, and efficiency CNC waterjet, plasma, and laser cutting technologies are usually employed. EDM (electrical discharge machining) could be also an option in some cases.
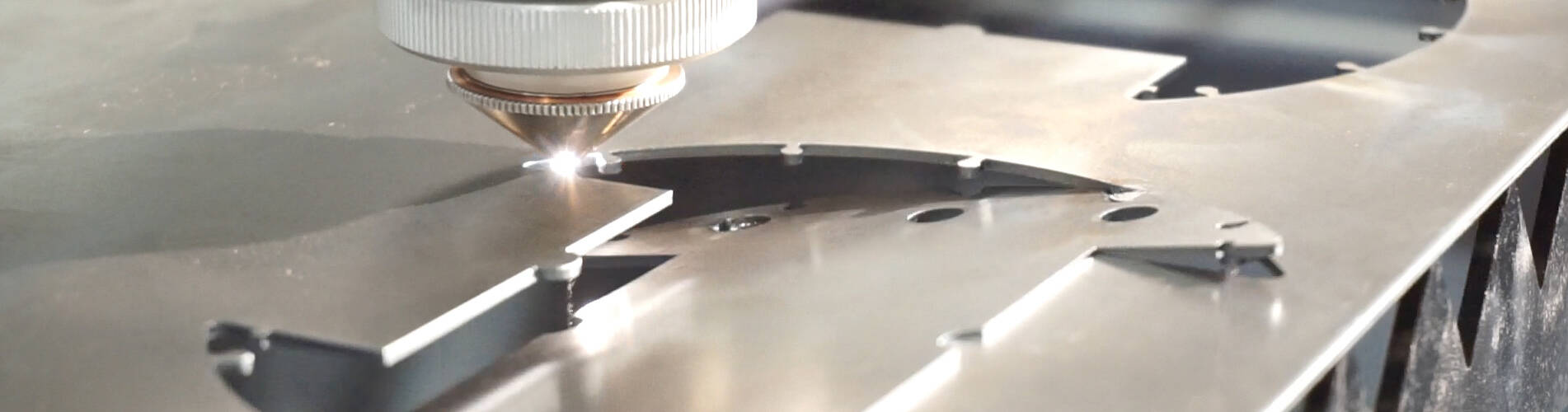
Laser Cutting
In laser cutting, a high-density laser beam is directed onto a workpiece to melt, vaporise, or burn through it, effectively cutting the material. Laser cutters are used for cutting, boring, and engraving. There are three types of lasers used in laser cutting; CO2 (carbon dioxide), Nd (neodymium), Nd:YAG (neodymium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet).
CO2 lasers have high energy efficiency and high power output ratio, and are used for cutting thin material, engraving, and boring. Nd lasers have high energy but low repetition efficiency. They are used for engraving, boring, and welding. Nd:YAG lasers have a very high power output and can cut thicker materials. However, they are more expensive to operate than CO2.
Laser cutters can work with aluminum, steel, copper, stainless steel, and other metals. They are best used for cutting thin workpieces (maximum thickness of 15 mm for aluminium and 6 mm for steel), engraving, and boring
Water-Jet Cutting
In water-jet cutting, a nozzle is used to focus a jet of water at very high pressures to cut a workpiece. For relatively soft material like rubber and wood, only water is used. A mixture of water and abrasive granular substances is used to cut harder material such as metals.
Water-jet cutting can cut material of various thicknesses. The maximum thickness that can be cut depends on the material. Of all CNC cutting methods, waterjet cutting is the most precise with tolerances between 0.05 mm and 0.1 mm. One of the reasons for its high precision is that unlike plasma and laser counterparts, waterjet cutting does not generate heat hence there is no heat affected zone in the workpiece.
Waterjet cutting is very versatile as it is used to cut hard material such as aluminum, steel, copper, stainless steel, and other metal alloys as well as softer materials like polymers, elastomers, wood, and foam.
More info at www.jmintek.com.